What Is A Quadcopter Drone?
Quadcopter drones have revolutionized the way we capture aerial views, conduct inspections, and even compete in drone racing. From capturing breathtaking aerial photography to revolutionizing industries, these versatile flying machines have captured the imagination of hobbyists and professionals alike. Their unique design—four fixed rotors arranged symmetrically—offers simplicity, stability, and exceptional maneuverability. In this guide, we explore what quadcopter drones are, their main components, types, differences from other aerial vehicles, how they fly, their advantages, applications, building tips, and answers to frequently asked questions.
What Is A Quadcopter Drone?
A quadcopter drone is an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) that uses four rotors for lift and propulsion. Unlike fixed-wing aircraft, quadcopters can take off and land vertically and hover in place. Their configuration—two rotors spinning clockwise and two counterclockwise—cancels out torque and provides stable flight control. This design, which was once experimental, has become a cornerstone for consumer, commercial, and industrial drone applications.

What are the main components of a quadcopter?
A well-designed quadcopter comprises several key components that work in harmony:
●Frame: The rigid structure that holds all the components together. Frames come in various shapes (X, H, etc.) and sizes depending on the drone’s intended use.
●Motors: Typically four brushless DC (BLDC) motors that power the rotors and provide the necessary thrust.
●Electronic Speed Controllers (ESC): Devices that regulate the power supplied to each motor based on signals from the flight controller.
●Propellers: Fixed-pitch blades attached to each motor; they convert rotational energy into lift.
●Flight Controller: The central “brain” of the drone that processes sensor data (gyroscopes, accelerometers, sometimes GPS) and translates pilot commands into motor speed adjustments.●Battery: Usually a rechargeable LiPo (lithium-polymer) battery that supplies the necessary power. Battery capacity directly affects flight time.
●Radio Receiver and Transmitter: For remote control communication between the pilot and the drone.
●Optional Components: Cameras, gimbals for stabilization, and FPV (first-person view) systems enhance the drone’s capabilities, particularly for aerial photography or racing.
●Sensors (Optional but common): GPS, obstacle avoidance, and cameras enhance functionality.
Types of Quadcopters
Quadcopters come in various designs based on their frame shape and intended purpose:
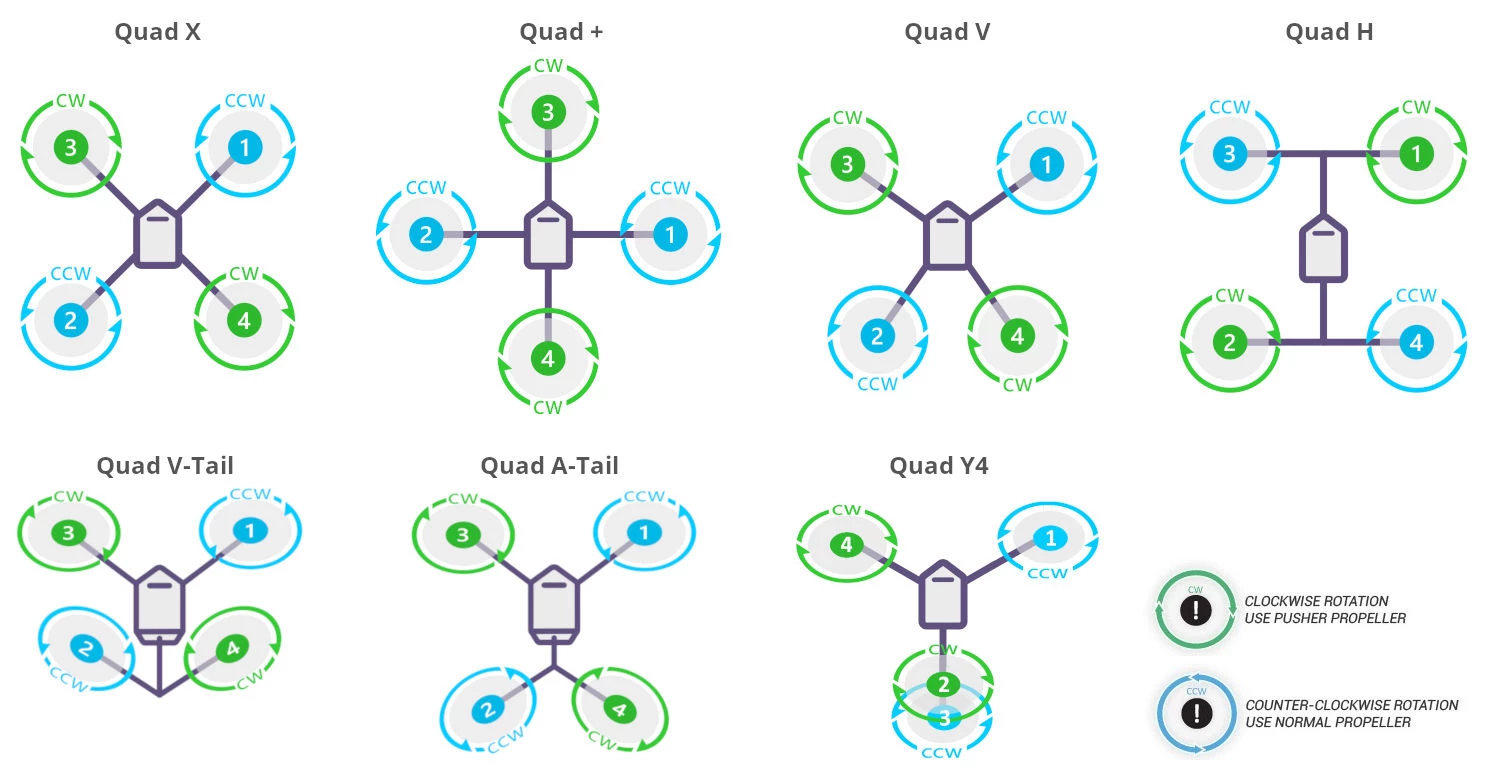
By design:
●X-Configuration: The most common design, offering balanced control and maneuverability.
●H-Configuration: Often provides enhanced stability and can be ideal for aerial photography.
●+ Configuration: Sometimes used for simpler control schemes in certain applications.
●Specialized Variants: Some designs incorporate variations like Y4 or V-tail for improved yaw control or payload capacity. Each type is optimized for specific uses such as recreational flying, professional filming, or competitive racing.
By applications:
●Mini Quadcopters: Compact (under 250g), ideal for indoor use (e.g., DJI Mini 3 Pro).
●Racing Quadcopters: Lightweight, agile, with FPV (First-Person View) systems for competitive racing.
●Photography Drones: Equipped with high-resolution cameras and gimbals (e.g., DJI Phantom).
●Commercial/Industrial Drones: Larger models for agriculture, surveying, or delivery (e.g., Matrice 300).
What is the difference between a drone and a quadcopter?
The term "drone" is a broader term that refers to any unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), land vehicle (UGV), or surface/underwater vehicle (USV) that can operate autonomously or be remotely controlled. A quadcopter is a specific type of drone that uses four rotors for propulsion. Therefore, all quadcopters are drones, but not all drones are quadcopters. Other types of drones include fixed-wing aircraft, single-rotor helicopters, and multi-rotor systems with more or fewer than four rotors (e.g., hexacopters with six rotors, octocopters with eight rotors).
What is the difference between a quadcopter and a helicopter?
Quadcopter uses four fixed-pitch rotors with differential speed control for movement. They are mechanically simpler, easier to control (especially for beginners), and are more compact. Helicopter typically has a single main rotor with variable pitch blades and a tail rotor for torque balance. Helicopters can be more efficient for heavy lifting but are mechanically more complex and generally require more skill to operate.
How Does a Quadcopter Fly?
A quadcopter's flight is a marvel of physics and engineering, relying on the principle of thrust and precise control of its four rotors. Here's a breakdown:
●Lift: All four rotors spin, generating downward airflow and thus upward thrust. When the total thrust generated by the rotors exceeds the quadcopter's weight, it takes off.
●Hovering: To hover in place, the flight controller adjusts the speed of all four rotors to generate just enough thrust to counteract gravity.
●Vertical Movement: To ascend, the speed of all four rotors is increased equally, generating more thrust than weight. To descend, the speed is decreased.
●Pitch (Forward/Backward Movement): To move forward, the rear rotors spin faster than the front rotors, tilting the quadcopter forward and generating forward thrust. Backward movement is achieved by increasing the speed of the front rotors.
●Roll (Sideways Movement): To move left, the right rotors spin faster than the left rotors, tilting the quadcopter to the left. Rightward movement is achieved by increasing the speed of the left rotors.
●Yaw (Rotation): To rotate clockwise (yaw right), two diagonally opposite rotors (e.g., front-right and back-left) spin faster, while the other two spin slower, creating a rotational force. Counter-clockwise rotation (yaw left) is achieved by reversing this.
The flight controller constantly monitors sensor data and makes micro-adjustments to the speed of each motor to maintain stability and execute the pilot's commands.
What are the advantages of a quadcopter?
Quadcopters offer several distinct advantages:
●Simplicity: With fewer moving parts than helicopters, they are easier to manufacture, maintain, and repair.
●Stability: Their design provides excellent hovering capabilities, making them ideal for aerial photography and videography.
●Maneuverability: Rapid changes in rotor speed allow for agile movements, crucial for racing and navigating tight spaces.
●Vertical Takeoff and Landing (VTOL): They can take off and land in confined areas without the need for a runway.
●Portability: Many quadcopters are relatively lightweight and foldable, making them easy to transport and deploy.
●Cost-Effective: Generally, quadcopters are more affordable than other UAV configurations, making them accessible to hobbyists and professionals alike.
What are the typical applications of quadcopters?
Quadcopters are used across a wide spectrum of fields:
●Aerial Photography and Videography: Their stability and ease of use have made them popular for capturing stunning images and cinematic video.
●Agriculture: Drones monitor crop health, spray pesticides, and perform soil analysis.
●Surveying and Mapping: Equipped with high-resolution cameras or LiDAR, they assist in creating accurate topographical maps.
●Delivery and Logistics: Emerging applications include delivering small packages to remote areas.
●Search and Rescue: Their ability to hover and maneuver in tight spaces makes them ideal for locating missing persons in challenging environments.
●Recreational Use: Hobbyists enjoy quadcopters for casual flying and racing.
●Inspection and Surveillance: They are deployed to inspect infrastructure, pipelines, and other critical assets.
●Law Enforcement and Public Safety: Assisting in crime scene investigation and emergency response.
How to build a quadcopter?
Building your own quadcopter can be a rewarding project. Here are the general steps:
●Select a Frame: Choose a frame size and configuration based on your intended use.
●Choose Motors and ESCs: Match motor specifications with propeller size and battery capacity. Ensure ESCs can handle the current draw.
●Flight Controller Setup: Install a flight controller with compatible sensors (gyroscope, accelerometer, GPS) and configure it using open-source firmware (e.g., Betaflight).
●Mount Propellers and Battery: Attach propellers securely and install the battery in a way that maintains the center of gravity.
●Wiring and Assembly: Connect motors to ESCs and then to the flight controller. Use a power distribution board if necessary.
●Testing and Calibration: Calibrate sensors and test motor responses in a controlled environment.
●First Flight: After thorough checks, perform a cautious maiden flight in an open and safe area. Gradually increase altitude and test basic controls.
●Note: Building a quadcopter requires technical knowledge and careful attention to detail. It's recommended to start with beginner-friendly guides and resources.
FAQs
What is a mini quadcopter?
A mini quadcopter (<250g) is a small and lightweight quadcopter, typically with a wheelbase (distance between opposite motors) of less than 200mm. They are often used for indoor flying, racing in tight spaces, or as a more portable option for outdoor fun.
What is a racing quadcopter?
A racing quadcopter is engineered for high speed and agility. They are often built with robust motors, customizable flight controllers, and are flown in first-person view (FPV) mode. These drones are popular in competitive drone racing leagues.
What is a big quadcopter drone?
A big quadcopter drone generally refers to larger models with a wheelbase of 500mm or more. These drones often have higher payload capacities, longer flight times, and are used for professional applications like aerial photography, surveying, and delivery.
Are quadcopters easy to fly for beginners?
Yes. Many quadcopters feature stability modes, altitude hold, and automated return-to-home functions that help beginners learn to fly safely. However, mastering manual controls for advanced maneuvers does require practice.
How long can a quadcopter fly on a single charge?
Flight time typically ranges from 10 to 30 minutes, depending on factors like battery capacity, payload weight, and environmental conditions. High-end models or those with extra batteries may achieve longer flight times.
How high do quadcopte Fly?
Quadcopters can fly at various altitudes, but regulations often limit them to below 400 feet (120 meters) in many countries. How fast can a quadcopter fly? Speed varies widely; racing models can exceed 100 mph (160 km/h), while standard consumer drones typically fly between 30 and 60 mph (50–100 km/h).
What factors affect a quadcopter's flight time and performance?
Factors include battery capacity, motor efficiency, propeller design, and environmental conditions like wind. What should I look for when buying a quadcopter? Consider factors like intended use, budget, flight time, and features such as GPS or camera quality.
How much does a quadcopter cost?
The cost of a quadcopter can vary significantly, ranging from under $50 for basic toy models to thousands of dollars for professional-grade drones with advanced features. Hobbyist drones typically cost between $100 and $1000.
Can quadcopters carry cameras?
Yes, many quadcopters are designed to carry cameras. These can range from integrated cameras for basic photography and videography to more advanced systems with high-resolution sensors and gimbal stabilization for professional-quality aerial footage.
Can I fly a quadcopter indoors?
Many mini quadcopters are designed for indoor use due to their small size and light weight. However, wind and obstacles must be considered when flying indoors.
Do I need a license to fly a quadcopter?
Regulations vary by country. In many regions (such as the US for drones under 250 grams), registration or a license is not required for recreational use. Commercial operations generally require certification and compliance with local aviation authorities.
What safety measures should be taken when flying a quadcopter?
Always follow local regulations, avoid flying near people or obstacles, and ensure proper maintenance of the drone.
Are there legal restrictions for flying quadcopters?
Yes, there are legal restrictions for flying quadcopters in most countries. These regulations often cover aspects like registration, pilot licensing, altitude limits, no-fly zones, privacy concerns, and commercial use. It is crucial to research and understand the specific regulations in your area before operating a quadcopter.
Conclusion
Quadcopter drones are versatile, user-friendly, and ideal for a range of applications—from breathtaking aerial photography and mapping to exhilarating drone racing and commercial inspections. Their simple yet robust design, characterized by four fixed rotors and differential thrust control, makes them easier to build, fly, and maintain than many other aerial vehicles. By understanding their components, how they fly, their advantages, and the crucial safety and legal considerations, you can safely and responsibly explore the exciting world of four-rotor flight. As a global leading lithium-ion battery manufacturer, Grepow offers high power and energy density quadcopter battery for all knids of quadcopter drones. If you have any questions or needs, please feel free to contact us at info@grepow.com.
Related Articles
-

What Is a Long Endurance Drone?
2025-04-16 -

Empowering Drone Training with Grepow’s Tailored Battery Solutions
2025-04-15 -

Four Specialized Lithium-Ion Battery Types Basis
2025-04-10
Related products
-

Tattu NEO Series Smart Batteries For Industrial Drones
-

350Wh/kg Series Semi-Solid State High Energy Density Battery Pack
-

4.45V Ultra High Voltage Semi-Solid State Battery