What Is a Long Range Drone?
Long-range drones are transforming industries by offering extended flight times, vast operational areas, and advanced surveillance capabilities. These unmanned aerial systems (UAS) are designed to cover long distances while maintaining high‑quality data transmission, making them indispensable for applications ranging from agriculture and mapping to aerial photography and emergency response.This article delves into the intricacies of long-range drones, exploring their technology, applications, regulatory landscape, and crucial considerations for those looking to harness their potential.
What Is a Long Range Drone?
A long-range drone is an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) capable of operating beyond the visual line of sight (BVLOS) and covering distances typically exceeding 20 kilometers. Unlike consumer drones designed for short-range photography, these drones prioritize endurance, advanced communication systems, and robust navigation. For example, fixed‑wing models and VTOL (Vertical Takeoff and Landing) drones are common choices because they combine endurance with the ability to take off and land in confined spaces. Key features include:
●Extended Battery Life: High-capacity lithium-polymer (LiPo) batteries, hydrogen fuel cells, or hybrid systems.
●Advanced Communication: Satellite links or cellular networks for BVLOS operations.
●Payload Flexibility: Customizable for cameras, sensors, or delivery mechanisms.
Industries like agriculture, logistics, and surveillance rely on long-range drones for tasks requiring vast coverage and reliability.
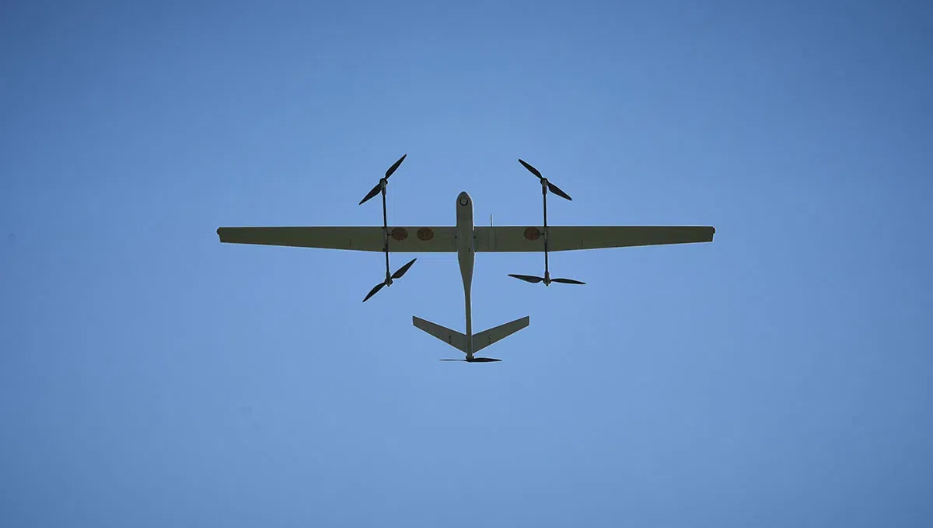

How Does Drone Range Drone Work?
Long‑range drone performance is underpinned by a suite of technologies designed to maximize efficiency and communication reliability:
Power Systems and Endurance
High‑capacity batteries, fuel‑efficient engines, or even hybrid power systems are key to providing the long flight times needed for extended missions. Lightweight, high‑energy‑density batteries and aerodynamic designs help reduce energy consumption.
Advanced Communication Systems
Maintaining a stable control and video transmission link is essential. Long‑range drones use advanced systems—often employing dual‑frequency (2.4GHz/5.8GHz) radio links, 4G/5G connectivity, or even satellite communications—to keep the drone connected to its ground control station over vast distances.
Navigation and Autonomy
These drones are equipped with high‑precision GPS and often incorporate autonomous flight modes, waypoint navigation, and obstacle avoidance systems. Such features enable the drone to safely operate beyond the pilot’s visual line of sight (BVLOS) and return home automatically in case of signal loss.
What's the Applications of Long Range Drones
Long-range drones have emerged as indispensable tools across a multitude of industries, extending operational capabilities and offering solutions to complex challenges.
Agriculture and precision farming
In agriculture and precision farming, long-range drones provide real-time insights into crop health, soil conditions, and irrigation needs across extensive areas, leading to enhanced productivity and reduced operational costs . They enable the precise application of pesticides, fertilizers, and herbicides, optimizing resource use and minimizing environmental impact . Furthermore, these drones assist in irrigation management by tracking system performance and identifying deficiencies, and they facilitate accurate yield predictions through the analysis of crop health and growth patterns . Even livestock monitoring can be improved with the wide coverage offered by long-range drones . The ability to efficiently manage vast agricultural lands makes this technology a cornerstone of modern sustainable farming practices.
Infrastructure inspection and monitoring
The infrastructure inspection and monitoring sector has also seen a significant impact from long-range drones. They can inspect miles of power lines, pipelines, and railways for leaks, structural issues, wear, or damage, reducing the need for manual inspections in hazardous or remote locations . Thales's UAS100, for instance, is optimized for linear infrastructure inspection . Additionally, these drones can examine bridges, dams, and wind turbines for maintenance needs, providing detailed visual and thermal data . Generating 3D topographic models for construction site planning and monitoring progress over large areas is another key application . By offering a safer and more efficient method for infrastructure assessment, long-range drones contribute to preventing failures and reducing maintenance expenditures.
logistics and delivery
In logistics and delivery, long-range drones offer the potential to autonomously transport goods over considerable distances, bypassing traffic congestion and reducing delivery times, particularly to remote or isolated areas . They can provide rapid delivery services for time-sensitive items such as pharmaceuticals and medical supplies, and transport packages to rural communities where traditional delivery methods are slow or inefficient . This capability is poised to revolutionize supply chains and improve accessibility to essential goods.
Search & rescue
Emergency response and search & rescue operations are significantly enhanced by the deployment of long-range drones. They can swiftly cover extensive areas to locate missing personnel, especially in hostile or inaccessible zones . Providing aerial views of disaster zones allows for better coordination of rescue efforts and assessment of infrastructure damage . These drones can also monitor areas affected by floods or landslides for survivors and assess hazardous environments such as active fire zones or chemical spills . Their speed and wide coverage make them invaluable in critical situations.
What's the BVLOS of Long Range Drone?
Beyond Visual Line of Sight (BVLOS) operation is a defining characteristic and a key enabler for many long-range drone applications. Traditionally, drone operations require the pilot to maintain a direct visual line of sight with the aircraft. BVLOS operations, however, allow drones to fly distances far beyond what the pilot can see, unlocking the true potential of long-range capabilities. However, BVLOS operations demand rigorous safety protocols and advanced systems such as detect‑and‑avoid (DAA) technologies and redundant communication links to ensure safety and regulatory compliance.
Regulatory Considerations for Long Range Drone
Operating long‑range drones comes with strict regulatory requirements that vary by region:
●FAA and Part 107: In the United States, drones are generally required to be flown within the visual line of sight. Operators wishing to perform BVLOS missions must obtain special waivers and meet stringent safety criteria, including robust DAA systems and secure communication links.
●International Standards: In Europe and other regions, similar BVLOS and remote ID regulations exist. Compliance with standards—such as those set by the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA)—ensures safe integration into national airspace systems.
●No-Fly Zones: Restricted near airports or sensitive areas.
●Insurance: Liability coverage for commercial operations.
●Pilot Training: Advanced licenses for BVLOS flights.
●Safety and Privacy:Additional regulatory issues include ensuring public safety, managing airspace congestion, and protecting data transmitted between the drone and the ground station. Always consult local aviation authorities before deployment.
How to Choose a Long-range Drone?
When selecting a long‑range drone, consider the following factors:
●Flight Range and Endurance: Assess the drone’s maximum range and flight time to ensure it meets your mission requirements.
●Communication and Control: Look for advanced transmission systems that provide stable, high‑resolution video feeds over long distances. Features like dual‑frequency transmission and anti‑interference capabilities are crucial.
●Payload and Sensor Options: Consider the types and weights of payloads the drone can carry. Whether you need high‑resolution cameras, thermal sensors, or specialized equipment, ensure the drone’s payload capacity matches your needs.
●Navigation and Autonomy: Evaluate the drone’s autonomous capabilities, including waypoint navigation, obstacle detection, and automatic return‑to‑home functions.
●Regulatory Compliance: Verify that the drone meets local regulatory requirements, including BVLOS waivers and Remote ID standards if applicable.
●Durability and Environmental Resistance: Consider the operating environment and choose a drone that can withstand the expected weather conditions.
●Cost and Maintenance: Factor in the initial purchase price, operational costs, and maintenance requirements. Long‑range drones can range from a few thousand dollars for simpler models to tens of thousands for advanced commercial systems.
Long Range Drone FAQ
What is the maximum range of long-range drones?
Maximum range varies widely. High‑end fixed‑wing and VTOL models can cover 100–200 km or more, while some advanced commerical systems have ranges exceeding hundreds of kilometers.
What factors affect a drone's range?
Key factors include battery capacity, payload weight and aerodynamics, environmental conditions (wind, temperature), signal strength, and the efficiency of the propulsion and communication systems.
How can I extend my drone's flight range?
Extending a drone's flight range can involve using higher-capacity batteries, reducing payload weight, flying in optimal weather conditions (minimal wind), ensuring a strong communication link, and potentially upgrading to more advanced communication systems or drone models designed for longer ranges.
How do long-range drones maintain communication?
Redundant systems: RF for short-range, switching to satellite or cellular networks at longer distances.
What payloads can long-range drones carry?
Payload capacities vary; many commercial models can carry from a few kilograms to over 25 kg. Common payloads include high-resolution cameras, thermal and multispectral sensors, LiDAR systems, and even cargo for delivery applications.
Do weather conditions affect long-range performance?
Yes. Adverse weather—such as high winds, extreme temperatures, or icing conditions—can reduce battery efficiency, alter aerodynamics, and degrade signal strength, thereby affecting flight range and stability.
What is the cost of long-range drones?
The cost of long-range drones can vary dramatically depending on their capabilities, features, and intended use. Basic long-range consumer drones might start in the low thousands of dollars, while high-end industrial long-range drones with advanced sensors and BVLOS capabilities can cost tens or even hundreds of thousands of dollars.
Conclusion
Long-range drones represent a significant advancement in unmanned aerial vehicle technology, offering transformative capabilities across a multitude of industries. As battery technology, communication systems, and regulatory frameworks continue to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative applications emerge, pushing the boundaries of what's possible from the skies. As a global leading lithium-ion battery manufacturer, Grepow offers high power and high energy density semi-solid state battery for industrial long-range drones. If you have any questions or needs, please feel free to contact us at info@grepow.com.
Related Articles
-

What Is a Long Endurance Drone?
2025-04-16 -

Empowering Drone Training with Grepow’s Tailored Battery Solutions
2025-04-15 -

Four Specialized Lithium-Ion Battery Types Basis
2025-04-10
Related products
-

330Wh/kg Series Semi-Solid State High Energy Density Battery Pack
-

350Wh/kg Series Semi-Solid State High Energy Density Battery Pack
-

4.45V Ultra High Voltage Semi-Solid State Battery