Smart Wearable Device Battery Charge Management
Lithium-ion batteries have the advantages of high energy density, high operating voltage, wide application temperature range, low self-discharge rate, long cycle life, and no pollution, which are in line with the smart wearable devices batteries requirements. Smart wearable devices refer to items that people wear every day, such as smart helmets, smart watches, smart rings, smart belts, smart insoles, belts, etc., with intelligent electronic design functions, and then quantitative analysis of the data to give a suggestion, reports, and recommendations. Smart wearable devices require a stable power supply system with a long standby duration and large capacity. Lithium-ion batteries have advantages of higher energy density (100~140w kg), smaller size (270 w.h/L), and higher operating voltage (3.6V, 3.8V), wide application temperature range (-10°C~45°C), low self-discharge rate (6~10%/month), long cycle life (300~2000 times), no pollution (no mercury, lead, cadmium), which are very suitable for use in smart wearable devices.

However, the structural characteristics of the lithium-ion battery are quite special, and the parameters of the charge and discharge must be strictly controlled, so the requirements for the power management chip are high. The SMG4056 is a highly integrated power management chip for single-cell Li-Ion battery charging that reliably and quickly adjusts the maximum charge current and cut-off current when managing the smart wearable battery.
1. Smart wearable device batteries charging feature
Working principle and characteristics of smart wearable devices Batteries
The charging and discharging process of the smart wearable device battery mainly relies on the lithium-ion intercalating and decoupling between the positive and negative polar compounds. During the whole charging and discharging process, lithium appears in the form of ions.
The smart wearable devices Batteries Charging characteristics
When charging a lithium-ion battery, it is necessary to check the battery voltage, battery temperature and set up a maximum charge time to ensure safety. Generally, the charging process of a lithium-ion battery can be divided into three steps: pre-charge, fast charge, and full charge.

WATTup wireless charging (Source: Energous)
The charging management chip detects the battery voltage before the starts. When it detects lower than 2.5V, it will enter into the pre-charging phase. The pre-charging current ICHG is approximately equal to 1/10 of the fast charging current (about 0.01, 0.1C). When the charging management chip detects that the battery voltage value is above 2.5V, the charging switches from constant current to constant voltage mode, as follows: the charging start phase goes with a constant current, about 0.1~1.0C, and when the battery voltage gets close at 4.1V~4.2V, the charging current ICHG is gradually reduced to near zero until the charging stopped. The battery temperature range is maintained in the range of 25~50 °C during the whole charging process when the temperature is higher than this range, the chip disconnects the charging circuit until the temperature recovers to the normal status.
2. SGM4056 main features and pin-foot description
SGM4056 is a highly integrated power management chip. The internal circuit mainly includes: input current monitor, battery voltage detector, temperature detector, and main controller, which supports smart wearable device battery pre-charge, constant current, and constant voltage charging.
Picture 1 SGM4056 chip pin diagram
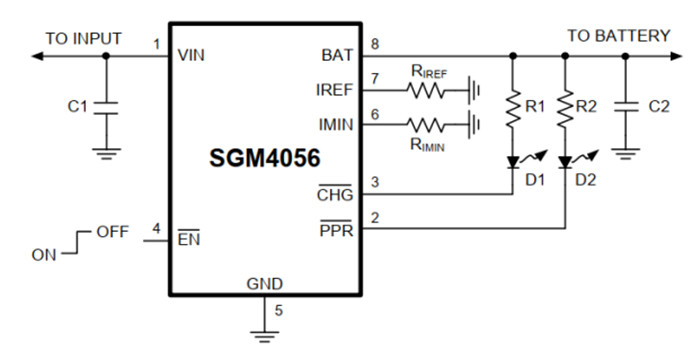
Table 2.1 Pin number from the pic. 1 and its function
| Pin | Name | Function |
| 1 | VIN | External power input pin |
| 2 | PPR | External AC adapter, power system OK indicator pin |
| 3 | CNG | Charging status indicator |
| 4 | EN | Charging enable |
| 5 | GND | Ground |
| 6 | IMIN | Cut-off charge current adjustment |
| 7 | IREF | Fast charge current adjustment |
| 8 | BAT | Battery output |
3. Typical application circuit design
According to the working principle and functional characteristics of the SGM4056 chip, combined with the characteristics of the smart wearable device products, the SGM4056 can be used to design the lithium-ion battery charge management circuit, which mainly completes the charging of the lithium-ion battery and the power supply to the smart wearable device system.
MCU only needs to be connected to the CHG pin to detect the charge status. Grepow is designing a 60mAh lithium-ion battery, the external VIN power supply is USB 5V DC, the EN pin pull-down resistor connected to ground, only when the 5V external power supply is connected to the SGM4056, the system enters into charging mode. Through the external fast charge resistor RIREF-130 kΩ, accuracy F, full charge cut-off resistance RIMIN: 130 kΩ, accuracy F, the theoretical fast charge current and full charge cut-off current are respectively calculated to be 93 mA and (1), (2) 13mA.
Using a multimeter and a programmable power supply, test and record the relationship among the charging cycle and the charging current, battery voltage, and CHG signal pin during charging of the smart wearable device battery. The detailed charging test data of the SGM4056 lithium-ion battery is shown in Appendix 1.
The smart wearable device battery charging fully meets the process of fast charging and then fully charging. When the battery voltage reaches the cut-off voltage of 4.2V, the charging current will rapidly decrease and enter into the full charge process. The full charge cut-off current is small, around 14mA, the fast charge current is 94mA, compared with the theoretically calculated 93mA and 13mA there is a 1mA error. When the charge cut-off current is lower than or equal to 14 mA, the output signal transitions from a low level to a high level, indicating that charging is completed.
Smart wearable device batteries conclusion
According to the functional characteristics of the SGM4056 chip, combined with the charging requirements of the lithium-ion battery, the SGM4056 external resistors RIREF and RIMIN can effectively program and monitor the charging current and the cut-off charging current of the smart wearable device battery. The charging curve shows that the SGM4056 charging management circuit can realize the requirement of fast charging and full charging, complete the charging of the lithium-ion battery, and ensure the stability of an intelligent wearable device system. If you are interested in our products, please don't hesitate to contact us at any time! Email: info@grepow.com Grepow Website: https://www.grepow.com/
Related Articles
-

What Is an Inspection Drone?
2025-04-21 -

The World's First Humanoid Robot Participation in Half Marathon
2025-04-16 -

What Is a Long Endurance Drone?
2025-04-16