High Voltage Batteries: Basics & Applications Guide
High voltage batteries are a relative concept in the battery-powered equipment market. Generally, there are two main types available:
1.Single High-Voltage Battery Cells: These are individual cells with a higher voltage and are primarily found in rechargeable lithium-ion batteries—often referred to in the industry as “LiHv.”
2.Series-Connected High Voltage Battery Packs: These packs are formed by connecting multiple cells in series and are commonly used in solar energy storage, electric vehicles, and other applications where voltages can range from 12V up to 100V or more.
This guide focuses on the former—high-voltage battery cells (LiHv cells). We will cover key parameters, applications, maintenance practices, and tips for selection and customization to help you understand this evolving technology and make informed procurement decisions.
What Are High Voltage Batteries?
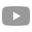
High voltage batteries are cells designed with a charging voltage higher than that of traditional batteries. While conventional rechargeable lithium-ion batteries typically have a full-charge voltage of 4.2V (with a nominal voltage around 3.7V or 3.6V), high voltage cells can reach full-charge voltages of 4.35V, 4.4V, or even 4.45V. Their corresponding nominal voltages may be 3.8V, 3.85V, or 3.95V. This performance improvement is achieved by optimizing electrode materials and electrolyte formulations, significantly boosting energy density—imagine a cup that can hold more water in the same volume.
Today’s high-end smartphones, true wireless (TWS) earbuds, laptops, and other portable electronics aiming for higher energy density and extended battery life often incorporate LiHv batteries.
Fundamental Parameters of High Voltage Batteries
Understanding high voltage batteries involves grasping several core parameters:
● Nominal Voltage vs. Full-Charge Voltage
Nominal Voltage: This represents the average voltage during normal operation, much like a battery’s “ID card.” For example, standard lithium-ion batteries are typically rated at 3.7V, while high voltage cells can be rated at 3.85V. The total voltage of a battery pack depends on the number of cells connected in series. For instance, a 4S (four-cell series) pack made with conventional cells would have a voltage of 4 × 3.7V = 14.8V, whereas a 4S pack with 3.85V high voltage cells would reach approximately 15.8V.
Full-Charge Voltage: This is the peak voltage achieved when the battery is fully charged. Conventional cells reach 4.2V, but high voltage cells can hit 4.4V (as seen in products like the Grepow 4.4V series).
Example: A high voltage cell with a nominal value of 3.95V offers a full-charge voltage about 6% higher than a standard cell, providing a stronger “initial push” for the device. For high-performance smart devices, selecting a battery with a higher charging voltage can enhance both endurance and output performance.
● Capacity and Energy Density
Capacity: Measured in milliampere-hours (mAh) or ampere-hours (Ah), this parameter indicates how long a battery can power a device on a single charge.
Energy Density: Expressed in watt-hours per kilogram (Wh/kg) or watt-hours per liter (Wh/L), energy density measures the amount of energy stored per unit weight or volume, which is crucial for achieving a lightweight design.
Example: By increasing both voltage and energy density, high voltage batteries can deliver extended battery life within the same volume. A TWS earbud, for instance, might see its operating time extend from 5 to 7 hours with a 4.45V high voltage cell.
● Internal Resistance (mΩ)
Internal resistance is akin to the resistance in a water pipe—the lower it is, the more efficiently current can flow. High voltage batteries are typically designed with low internal resistance (for example, Grepow batteries often have an internal resistance of less than 20mΩ), which reduces heat generation and enhances charge/discharge efficiency.
● Cycle Life – Balancing Longevity and Cost-Effectiveness
Cycle life refers to the number of complete charge/discharge cycles a battery can undergo before its capacity degrades significantly. Premium high voltage batteries (such as those from Grepow) can maintain over 80% of their initial capacity after 500 cycles, comparable to standard batteries.
● Discharge Rate – Power Output
The discharge rate, often expressed as the C-rate, describes the battery’s ability to release energy rapidly. A higher C-rate means stronger instantaneous power output, which is essential for devices like drones during takeoff, ignition boosters in vehicles, and high-performance electric equipment.
● Safety and Thermal Management
Battery Management System (BMS): A robust BMS prevents overcharge, over-discharge, short circuits, and overcurrent situations, ensuring safe operation.
Thermal Management Design: Under high load, batteries generate significant heat. Effective thermal management and heat dissipation are critical in minimizing risks associated with overheating.
Typical Applications of High Voltage Batteries
High voltage single cells are used in a variety of fields thanks to their high energy density and excellent electrical performance:
Consumer Electronics: Devices such as smartphones, tablets, laptops, and smartwatches benefit from high voltage batteries by achieving lightweight designs and extended battery life.
Premium Earbuds and Portable Devices: TWS earbuds, for example, use high voltage cells to deliver a stable power supply and faster charging speeds.
Research and Development: High voltage batteries offer a broader range of parameters for new technology and experimental projects, meeting specialized application demands.
Maintenance Practices for High Voltage Batteries
To keep high voltage batteries operating at their best and to extend their lifespan, follow these maintenance tips:
➖Storage
Optimal Storage Charge: When storing batteries for an extended period, maintain about a 50% charge.
Temperature Control: Avoid high temperatures. Ideally, store batteries at room temperature; ambient temperatures above 25℃ can accelerate internal chemical reactions, leading to irreversible capacity loss.
➖Avoid Overcharge and Over-Discharge
Proper Charging: Always use a charger specifically designed for high voltage batteries and adhere strictly to the manufacturer’s recommended charging voltage. Standard chargers may not fully charge a high voltage battery.
Prevent Over-Discharge: Regularly monitor the battery’s charge level to avoid depleting it completely. Note that the discharge cutoff voltage for high voltage batteries is generally higher (e.g., 3.0V compared to 2.75V for standard cells), so always confirm the recommended values with your supplier.
➖Maintain Appropriate Operating Temperature
Heat Dissipation: Ensure that devices using high voltage batteries have proper thermal management, especially under heavy loads.
Environmental Considerations: Avoid prolonged use or storage in extreme temperatures.
➖Regular Inspection and Maintenance
Status Monitoring: Utilize a BMS to continuously monitor battery health and quickly detect any anomalies.
Periodic Checks: Regularly test key parameters like internal resistance and capacity to preempt potential issues.
How to Choose the Right High Voltage Battery
When selecting or customizing a high voltage battery, consider the following factors:
Application Requirements
Device Needs: Evaluate the energy consumption, size, weight, and endurance requirements of your device to determine the optimal charging voltage and capacity.
Operating Environment: Take into account factors such as ambient temperature, humidity, and vibration to ensure stable battery performance in real-world conditions.
Parameter Matching and Technical Specifications
Voltage Parameters: Ensure that both the charging voltage and nominal voltage of the high voltage battery match your device’s specifications.
Performance Metrics: Pay attention to the discharge rate, cycle life, internal resistance, and energy density to confirm that the battery will perform reliably over extended use.
Customization and Supplier Selection
Customized Solutions: If standard products do not meet your specific needs, consider custom battery solutions.
Professional Suppliers: Choose suppliers with proven expertise and robust quality control processes.
FAQ
Q1: What distinguishes high voltage batteries from traditional lithium-ion batteries?
A: High voltage batteries feature a higher charging voltage (4.35V, 4.4V, or 4.45V) compared to the typical 4.2V of standard lithium-ion batteries. Their elevated nominal voltage increases energy density and overall performance.
Q2: Can high voltage batteries be mixed with standard batteries?
A: No. Mixing batteries with different voltages can lead to device damage and necessitate the replacement of the entire battery pack.
Q3: Are high voltage batteries compatible with all devices?
A: Compatibility depends on the device’s circuit design. It is essential to match the voltage, current, and connector specifications. Customized solutions may help address compatibility challenges.
Q4: Are high voltage batteries more dangerous?
A: Safety is determined by the cell design and protection circuitry. High-quality products, such as Grepow’s high voltage batteries, are UL/CE certified and feature multiple layers of protection.
Q5: What safety precautions should be observed when using high voltage batteries?
A: Key precautions include avoiding overcharge, over-discharge, excessive temperature, and physical damage. Use the manufacturer’s designated charger and BMS, and conduct regular maintenance checks.
Q6: Do high voltage batteries have a shorter lifespan?
A: No. Premium high voltage batteries, like those from Grepow, employ material optimization to ensure their lifespan is comparable to that of standard batteries.
Q7: How can the cycle life of a high voltage battery be determined?
A: Manufacturers provide cycle life data, and regular monitoring of capacity degradation in actual use can help assess battery life. Choosing products with proven market performance is advisable.
Q8: What unique advantages do Grepow high voltage batteries offer?
A: Grepow’s range includes various models with charging voltages from 4.35V to 4.45V and elevated nominal voltages. Coupled with mature customization services and stringent quality control, these batteries deliver high performance and safety for demanding applications.
Conclusion
High voltage batteries represent a significant advancement in next-generation energy storage technology. With their high energy density, superior power output, and flexible customization options, they are playing an increasingly vital role in consumer electronics, robotics, and various research projects. Whether you are new to battery technology or a professional seeking high-performance, customized solutions, this guide provides a thorough overview of the fundamentals, parameters, applications, maintenance, and selection of high voltage batteries.

Choosing the right high voltage battery can enhance device performance and ensure long-term system stability. As a leader in the industry, Grepow has a proven track record in remote-controlled models, FPV racing, and research projects—helping customers achieve efficient and stable power solutions. We look forward to exploring the limitless potential of high voltage batteries with you. For further professional consultation and customization services, please contact us at info@grepow.com.
Related Articles
-

CATL Chairman Yuqun Zeng Awarded Nobel Prize for Sustainable Development Contributions
2023-11-10 -
Resistance and Conductivity in Electric Batteries: A Simplified Explanation
2022-12-28 -

What Is A Soft Pack Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) Battery
2022-12-16
Related products
-

3.8V/4.35V High Voltage 30C Lipo Battery Cells
-

3.8V/4.35V High Voltage 8C Lipo Battery Cells
-

3.95V/4.45V High Voltage Cells